Understanding Real-Time Market Data Feeds: A Comprehensive Guide
In the fast-paced world of financial markets, access to real-time data can mean the difference between profit and loss. Real-time market data feeds serve as the lifeblood of modern trading platforms, delivering instantaneous price updates, volume information, and market depth to traders worldwide. This comprehensive guide explores the technical foundations, practical applications, and critical considerations for leveraging real-time market data effectively.
What Are Real-Time Market Data Feeds?
Real-time market data feeds are continuous streams of financial information transmitted from exchanges and market makers to end users with minimal delay. Unlike delayed data, which may lag by 15-20 minutes, real-time feeds provide immediate access to market movements, enabling traders to make informed decisions based on current market conditions.
These feeds typically include essential information such as last traded price, bid and ask prices, trading volume, time stamps, and order book depth. For active traders and institutions, this immediate access to market information is not just convenient—it's essential for executing strategies that depend on split-second timing.
Key Insight
The quality and speed of your market data feed directly impacts your ability to identify opportunities and execute trades effectively. Even milliseconds of latency can affect trading outcomes in highly competitive markets.
Types of Market Data Feeds
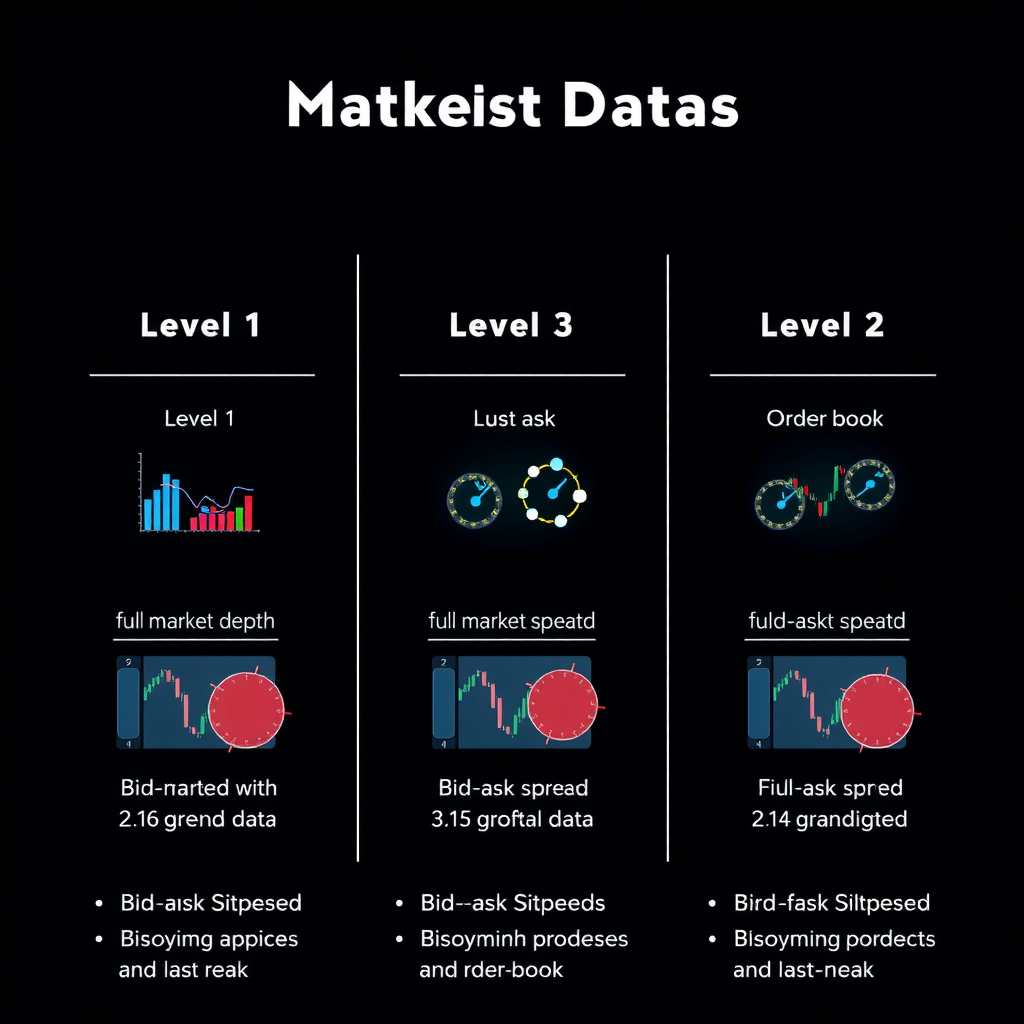
Level 1 Data
Level 1 data represents the most basic tier of market information, providing the best bid and ask prices along with the last traded price and volume. This data level is sufficient for casual traders and long-term investors who don't require deep market insights. Most retail trading platforms offer Level 1 data as part of their standard package, making it accessible to traders at all experience levels.
While Level 1 data offers a snapshot of current market conditions, it doesn't reveal the full picture of supply and demand dynamics. Traders using only Level 1 data may miss important signals about market depth and potential price movements that become apparent with more detailed information.
Level 2 Data
Level 2 data, also known as market depth or order book data, provides a more comprehensive view of market activity. This feed displays multiple price levels beyond the best bid and ask, showing the quantity of orders waiting at each price point. For active traders, this information is invaluable for understanding market liquidity and identifying potential support and resistance levels.
With Level 2 data, traders can observe the order flow and gauge market sentiment more accurately. Large orders sitting in the book can indicate strong support or resistance, while rapid changes in the order book may signal impending price movements. This enhanced visibility makes Level 2 data essential for day traders and scalpers who need to understand short-term market dynamics.
Time and Sales Data
Time and sales data, often called the tape, provides a chronological record of every executed trade. This feed includes the price, volume, and exact timestamp of each transaction, allowing traders to analyze trading patterns and identify institutional activity. By studying the tape, experienced traders can detect accumulation or distribution patterns that may not be visible in standard price charts.
Understanding Latency and Its Impact
Latency refers to the time delay between when market data is generated at the exchange and when it reaches your trading platform. In modern electronic markets, this delay is measured in milliseconds, but even these tiny fractions of a second can significantly impact trading performance, especially for high-frequency strategies.
Several factors contribute to overall latency, including network infrastructure, geographic distance from exchange servers, data processing overhead, and the efficiency of your trading platform. Professional traders often invest in co-location services, placing their servers physically close to exchange data centers to minimize latency and gain a competitive edge.
Network Infrastructure Considerations
The quality of your internet connection plays a crucial role in data feed performance. A stable, high-bandwidth connection with low jitter ensures consistent data delivery without interruptions or delays. Many serious traders opt for dedicated fiber connections or redundant internet services to maintain reliable access to market data even if one connection fails.
Beyond raw bandwidth, the routing path between your location and the data source matters significantly. Data traveling through fewer network hops experiences less latency and fewer potential points of failure. Some data providers offer multiple connection points, allowing you to choose the most efficient route based on your geographic location.
Choosing the Right Data Provider
Selecting an appropriate market data provider requires careful consideration of several factors. The ideal provider depends on your trading style, the markets you trade, your budget, and your technical requirements. Understanding these factors helps ensure you get the data quality and features necessary for your specific needs.
Market Coverage
Different providers offer varying levels of market coverage. Some specialize in specific asset classes like equities or futures, while others provide comprehensive coverage across multiple markets and exchanges. If you trade internationally or across different asset classes, ensure your chosen provider offers reliable data for all markets you need to monitor.
Consider not just the breadth of coverage but also the depth of data available for each market. Some providers may offer basic price data for many markets but provide detailed order book information only for select exchanges. Match the provider's offerings to your specific trading requirements to avoid paying for unnecessary data or lacking critical information.
Data Quality and Reliability
Data quality encompasses accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Reliable providers implement robust quality control measures to ensure data integrity, including validation checks, redundant data sources, and rapid error correction. Poor quality data can lead to incorrect trading decisions and missed opportunities, making this a critical selection criterion.
Reliability extends beyond data quality to include uptime and service availability. Your data provider should maintain high availability standards with minimal downtime, especially during critical trading hours. Look for providers with proven track records, redundant infrastructure, and clear service level agreements that guarantee performance standards.
Important Consideration
Always test a data provider's service during your typical trading hours before committing to a long-term contract. Performance can vary significantly based on time of day and market conditions.
API Integration and Technical Implementation
Modern market data feeds typically connect to trading platforms through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). These interfaces define how your software communicates with the data provider's servers, requesting and receiving market information. Understanding API integration is essential for anyone building custom trading applications or connecting to professional data services.
REST APIs vs. WebSocket Connections
REST APIs use a request-response model where your application explicitly requests data and receives a response. While suitable for historical data retrieval and occasional updates, REST APIs are less efficient for real-time streaming due to the overhead of repeated requests. Each request requires establishing a connection, sending headers, and processing responses, introducing latency and consuming bandwidth.
WebSocket connections provide a more efficient solution for real-time data streaming. Once established, a WebSocket connection remains open, allowing the server to push data to your application as soon as it becomes available. This persistent connection eliminates the overhead of repeated requests and enables true real-time data delivery with minimal latency. Most modern trading platforms use WebSocket connections for their primary data feeds.
Data Format and Parsing
Market data feeds typically deliver information in standardized formats such as JSON, XML, or binary protocols. JSON has become increasingly popular due to its human-readable structure and widespread support across programming languages. However, binary protocols offer superior performance for high-frequency applications where every microsecond counts.
Efficient data parsing is crucial for maintaining low latency. Your application must quickly decode incoming messages, extract relevant information, and update internal data structures without introducing delays. Optimized parsing routines and efficient data structures can significantly impact overall system performance, especially when processing high-volume feeds.
Best Practices for Maintaining Reliable Connections
Maintaining a stable, reliable connection to your market data feed requires implementing several best practices. These practices help ensure continuous data flow even in the face of network issues, server problems, or other technical challenges that might disrupt your trading operations.
Implementing Automatic Reconnection
Network interruptions are inevitable, making automatic reconnection logic essential for any serious trading application. Your software should detect connection failures immediately and attempt to reconnect using an exponential backoff strategy. This approach prevents overwhelming the server with rapid reconnection attempts while ensuring your application quickly restores its data feed when the network recovers.
During reconnection, your application must handle the gap in data appropriately. Depending on your trading strategy, you might need to request historical data to fill the gap, reset your analysis, or take other actions to ensure data consistency. Clear reconnection procedures prevent trading on stale or incomplete information.
Monitoring Connection Health
Continuous monitoring of connection health helps identify issues before they impact trading. Implement heartbeat mechanisms that regularly verify the connection is active and responsive. Track metrics such as latency, message rates, and error frequencies to detect degrading performance that might indicate network problems or server issues.
Set up alerts for critical connection events such as disconnections, high latency, or missing data. These alerts enable rapid response to problems, minimizing downtime and potential trading losses. Many professional traders maintain detailed logs of connection events for troubleshooting and performance analysis.
Redundancy and Failover
For critical trading operations, implementing redundant data connections provides insurance against single points of failure. Maintain connections to multiple data sources or use providers that offer redundant connection points. If your primary connection fails, your application can seamlessly switch to a backup connection, ensuring continuous market access.
Redundancy extends beyond network connections to include backup power supplies, redundant internet service providers, and even backup trading locations. The level of redundancy appropriate for your operation depends on your trading volume, strategy sensitivity to downtime, and risk tolerance.
Cost Considerations and Subscription Models
Market data costs vary dramatically based on the level of service, market coverage, and data depth required. Retail traders might access basic real-time data for free or minimal monthly fees through their broker, while professional traders and institutions may spend thousands of dollars monthly for comprehensive, low-latency feeds across multiple markets.
Understanding the pricing structure helps you budget appropriately and avoid unexpected costs. Some providers charge per exchange or market, while others offer bundled packages. Additional fees may apply for historical data access, API usage beyond certain limits, or premium features like Level 2 data. Carefully review the pricing terms to ensure they align with your trading needs and budget.
Professional vs. Non-Professional Designations
Many exchanges and data providers distinguish between professional and non-professional users, with significantly different pricing for each category. Non-professional status typically applies to individual traders using data solely for personal investment decisions. Professional designation covers anyone using data for business purposes, managing others' money, or distributing data to third parties.
The cost difference between professional and non-professional data can be substantial, sometimes ten times higher for professional access. Ensure you understand the qualification criteria and subscribe to the appropriate tier. Using non-professional data for professional purposes violates licensing agreements and can result in significant penalties.
Conclusion
Real-time market data feeds form the foundation of modern electronic trading, providing the information necessary to make informed decisions in fast-moving markets. Understanding the different types of data feeds, latency considerations, and technical implementation requirements helps traders choose appropriate solutions for their specific needs.
Whether you're a casual investor using basic Level 1 data or a professional trader requiring ultra-low-latency institutional feeds, selecting the right data provider and implementing robust connection management practices ensures reliable access to the market information you need. As markets continue to evolve and technology advances, staying informed about data feed options and best practices remains essential for trading success.
By carefully evaluating your requirements, understanding the technical aspects of data delivery, and implementing proper monitoring and redundancy measures, you can build a reliable market data infrastructure that supports your trading objectives and helps you stay competitive in today's electronic markets.